أتلانتا، الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية (CNN)-- لم تكن اليابان وراء لعبة "Space War!" التي تعتبر أول لعبة فيديو على الكمبيوتر ابتكرت عام 1962 في معهد ماساتشوستس التقني "MIT".
ولكن ومنذ ذلك الحين قامت اليابان باعتناق مجال ألعاب الفيديو على مدى عقود، لتصبح جزءاً أساسياً من ثقافتها، فبدءاً من لعبة "سوبر ماريو" وصولاً إلى ألعاب أجهزة "غيم بوي".
وأشار خبير ألعاب الفيديو بلايك جي هاريس، إلى أن "ألعاب الفيديو لم تكن لتنمو كقطاع مستقل لولا اليابان، فلم تساهم أي دولة أخرى بهذا المجال بدءاً بالبرمجيات والمعدات وحتى نشر ثقافة الألعاب."
لكن دور اليابان قل مع بدء الألفية الجديدة، بالأخص ومع انتشار هذه الألعاب حول العالم فكان من الطبيعي ألا تحتكر دولة معينة هذه التجارة، لكن يبدو وأن اليابان تعود تدريجياً اليوم للصدارة، إذ أصبح "بلاي ستيشن 4" الذي أصدر عام 2013، أكثر أجهزة ألعاب الفيديو مبيعاً، وهو الجهاز الوحيد إلى الآن الذي يمكن وصله بجهاز للواقع الافتراضي "Sony PSVR".
كما أن نينتندو تحطّم أرقاماً قياسية بمبيعات جهاز "Switch"، الذي ترافقه لعبة "Legend of Zelda"، التي لقيت نقداً إيجابياً.
إليكم قائمة اختارتها CNN لأبرز الاختراعات في عالم ألعاب الفيديو:
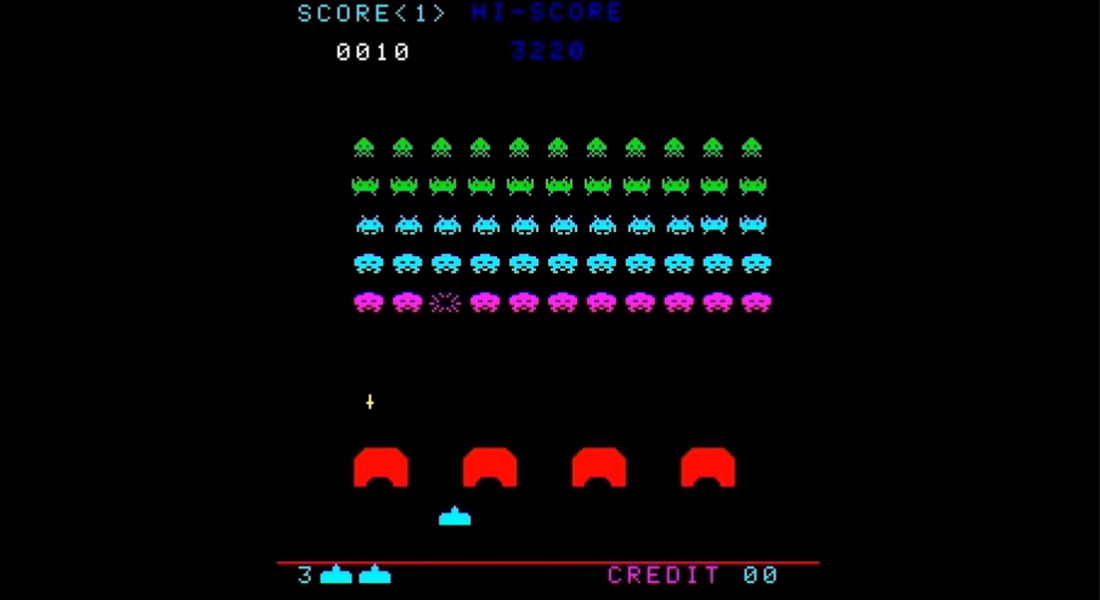
"Space Invaders" بأجهزة صالات الألعاب عام 1978، صنّعتها شركة "Taito"، التي ولّدت الهوس بألعاب الفيديو في اليابان.

"Pac-Man" بأجهزة صالات الألعاب عام 1980، التي صنّعتها شركة "Namco"، اللعبة انتشرت بشكل واسع وفي التسعينيات قامت شركة "Twin Galaxies" التي تتبع الأرقام القياسية لألعاب الفيديو، بقياس عدد المرات التي لعبت بها هذه اللعبة خلال القرن العشرين، والنتيجة كانت: 10 مليارات مرة!

"Family Computer" جهاز لألعاب الفيديو المنزلية صنعته شركة "نينتندو" عام 1983، عرف هذا الجهاز باسم "Famicom" وكان موجوداً في 37 في المائة من منازل اليابان، والبرمجية المستخدمة بهذا الجهاز "NES" منحت طرف الخيط لصناعة ألعاب الفيديو الأمريكية.
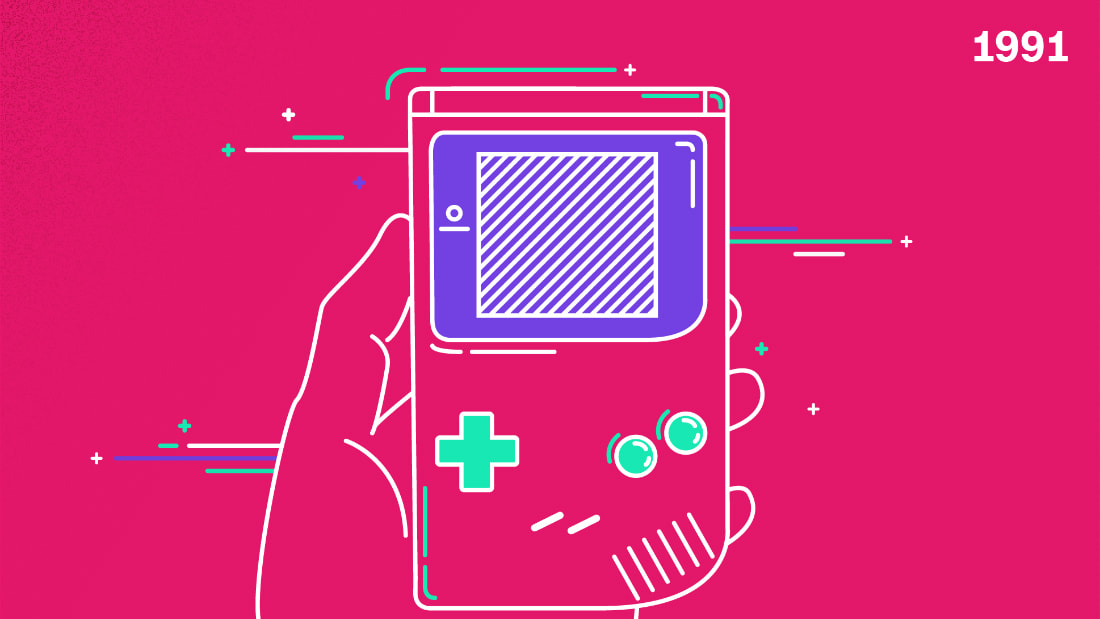

"غيم بوي" جهاز ألعاب الفيديو المتنقّل قدّمته نينتندو عام 1991، ليصبح هذا الجهاز المدخل الرئيسي لألعاب الفيديو المتنقّلة، أما تصميمه فأصبح أيقونة بعصره.

"Sonic the Hedgehog" قدّمته "سيغا" عام 1991، كانت "سيغا" من أبرز الأسماء أيضاً في عالم ألعاب الفيديو اليابانية، وتنافست مع نينتندو لتقدم لعبة "دونكي كونغ" في صالات الألعاب عام 1981.
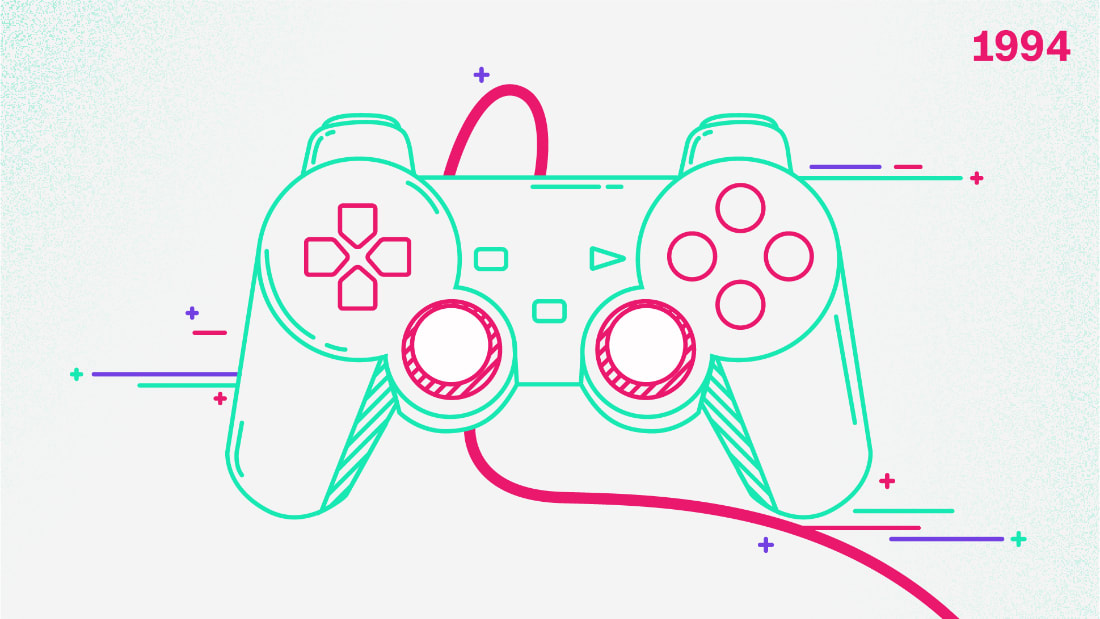
جهاز "سوني بلاي ستيشن" قدّمته "سوني: عام 1994، لتقدّم معه عالم الأقاص المدمجة "CD-ROM" التي سمحت بسعة أكبر وسعر أرخص في عالم الألعاب، مقارنة بالأشرطة التي كانت مستخدمة بالأجهزة السابقة.
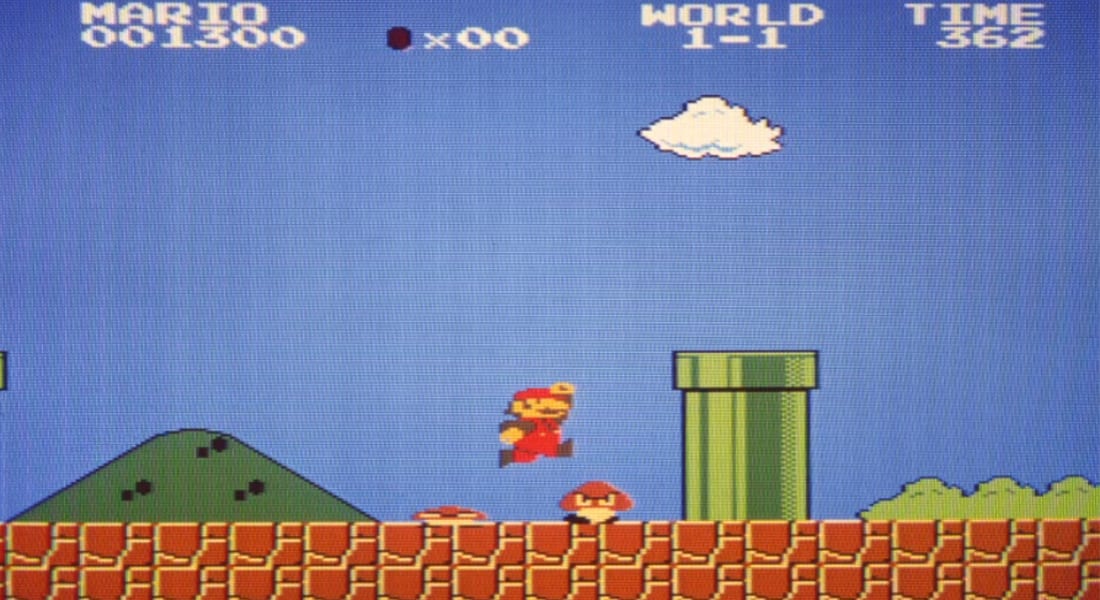

لعبة "Super Mario 64" قدّمتها "نينتندو" عام 1996، ورغم أن كلمة "3D" كانت تستخدم لوصف الألعاب، إلا أن تقنية الأبعاد الثلاثية لم تكن موجودة بعد آنذاك، وفي ذلك الوقت بدأت "سوني" و"مايكروسوفت" بالتنافس ضد نينتندو لتقوما بإخراج "سيغا" من خارج عالم صناعة أجهزة ألعاب الفيديو.
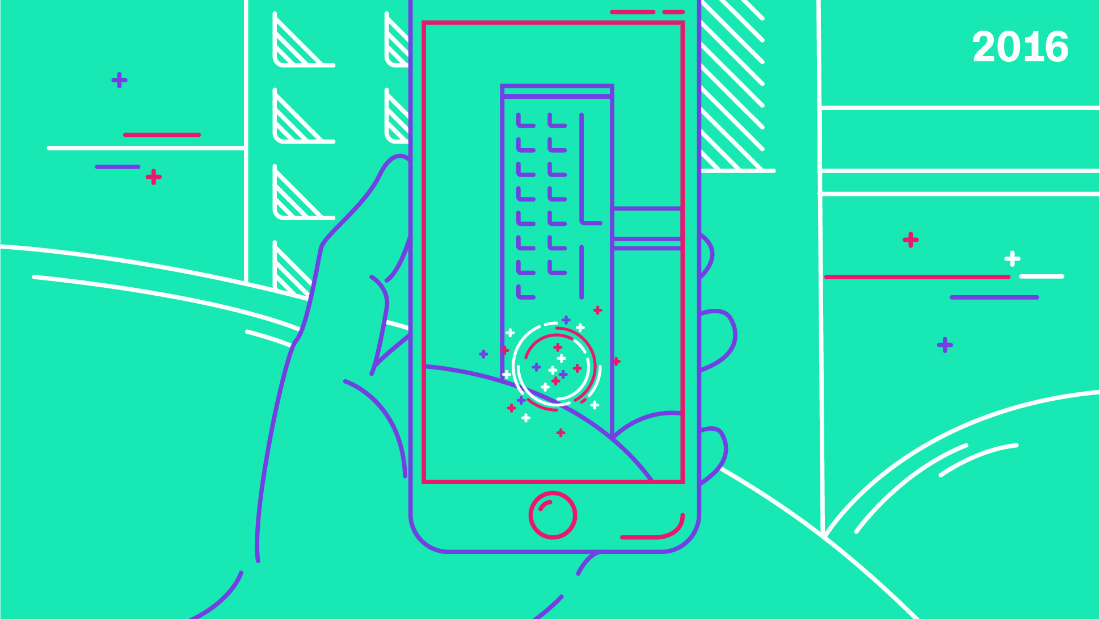
لعبة " Pokémon Go" قدّمتها شركة "Niantic" الأمريكية لأنظمة تشغيل "iOS" وأندرويد عام 2016، وحققت هذه اللعبة أرقام تحميل قياسية، ليبدأ اللاعبون بالتجول في الشوارع، بل ووقوع بعض الحوادث أثناء اللعب، اللعبة تمتاز بإدخال تقنية الواقع المدمج لتساهم بانتشارها بشكل واسع حول العالم.